Tutorial: Running IDAES model in FOQUS¶
The NETL’s Institute for the Design of Advanced Energy Systems is developing an equation-oriented framework for simulation and optimization of energy systems. A library of unit models is available to create and solve process flowsheets, therefore, a tutorial has been developed in FOQUS to import IDAES unit models, build a flowsheet, and simulate it.
The case study consists of the separation of Toluene-Benzene mixture (Figure 1). First the mixture is heated to 370K, and then separated in the Flash Tank. Consider the following process flowsheet that has been developed in FOQUS, using IDAES :
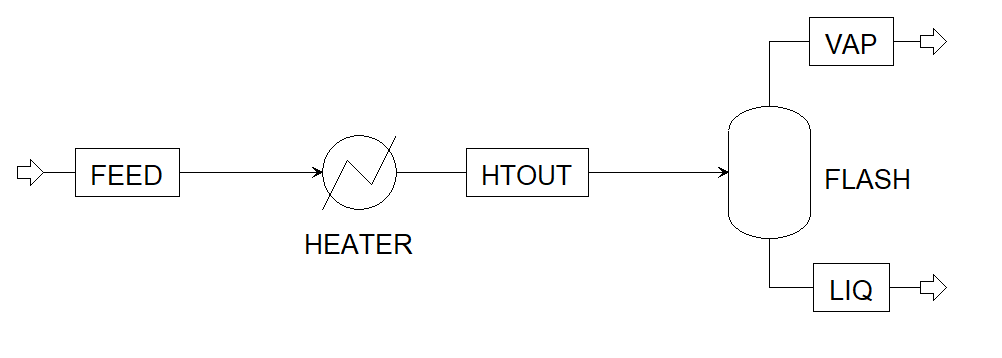
Figure 1: Heater Flash Flowsheet¶
Feed Conditions:
Flowrate = 0.277778 mol/s
Temperature = 353 K
Pressure = 101325 K
Benzene Mole Fraction = 0.4
Toluene Mole Fraction = 0.6
Heater Specification:
Outlet Temperature (HTOUT stream) = 370 K
Flash Specification:
Heat Duty = 0 W
Pressure Drop = 0 Pa
The following steps show how to import Python, Pyomo, and IDAES libraries and models, build the flowsheet, select input variables, and solve the simulation in FOQUS:
Instructions¶
Open FOQUS, and under the Flowsheet Tab, create a Node named “Flowsheet”.
Open the Node Editor and let the Model Type be “None”.
Add the following input variables with their corresponding values in the Node Editor:
heater_inlet_molflow: 0.277778 mol/sheater_inlet_pressure: 101325 Paheater_inlet_temperature: 353 Kheater_inlet_benzene_molfrac: 0.4heater_inlet_toluene_molfrac: 0.6heater_outlet_temperature: 370 Kflash_heat_duty: 0 Wflash_pressure_drop: 0 PaAdd the following output variables in the Node Editor:
heater_heat_dutyWflash_liq_molflowmol/sflash_liq_pressurePaflash_liq_temperatureKflash_liq_benzene_molfracflash_liq_toluene_molfracflash_vap_molflowmol/sflash_vap_pressurePaflash_vap_temperatureKflash_vap_benzene_molfracflash_vap_toluene_molfracAs stated in previous tutorials, the FOQUS simulation node allows the user to type a python script under the Node Script option. In this node script section, this tutorial shows how to import python libraries, Pyomo libraries, IDAES libraries and models, build and solve the flowsheet. Note that in this example, process conditions are fixed in order to have 0 degrees of freedom. Hence, the optimization actually gets solved as a simulation problem. A critical step is to link the FOQUS variables (input and output) to the IDAES mathematical model, thus, setting the inlet conditions of the process before solving the simulation problem. Finally, under Node Script, set Script Mode to “Post”. This will ensure that the node script runs after the node simulation. Enter the following code:
1# Import objects from pyomo package 2from pyomo.environ import ConcreteModel, SolverFactory,TransformationFactory, value 3 4import pyutilib.subprocess.GlobalData 5pyutilib.subprocess.GlobalData.DEFINE_SIGNAL_HANDLERS_DEFAULT = False 6 7# Import the main FlowsheetBlock from IDAES. The flowsheet block will contain the unit model 8 9import idaes 10from idaes.core.flowsheet_model import FlowsheetBlock 11 12# Import the BTX_ideal property package to create a properties block for the flowsheet 13from idaes.generic_models.properties.activity_coeff_models import BTX_activity_coeff_VLE 14 15# Import heater unit model from the model library 16from idaes.generic_models.unit_models.heater import Heater 17 18# Import flash unit model from the model library 19from idaes.generic_models.unit_models.flash import Flash 20 21# Import methods for unit model connection and flowsheet initialization 22from pyomo.network import Arc, SequentialDecomposition 23 24# Import idaes logger to set output levels 25import idaes.logger as idaeslog 26 27# Create the ConcreteModel and the FlowsheetBlock, and attach the flowsheet block to it. 28m = ConcreteModel() 29 30m.fs = FlowsheetBlock(default={"dynamic": False}) # dynamic or ss flowsheet needs to be specified here 31 32# Add properties parameter block to the flowsheet with specifications 33m.fs.properties = BTX_activity_coeff_VLE.BTXParameterBlock(default={"valid_phase": 34 ('Liq', 'Vap'), 35 "activity_coeff_model": 36 "Ideal"}) 37 38# Create an instance of the heater unit, attaching it to the flowsheet 39# Specify that the property package to be used with the heater is the one we created earlier. 40m.fs.heater = Heater(default={"property_package": m.fs.properties}) 41 42m.fs.flash = Flash(default={"property_package": m.fs.properties}) 43 44# Connect heater and flash models using an arc 45m.fs.heater_flash_arc = Arc(source=m.fs.heater.outlet, destination=m.fs.flash.inlet) 46 47TransformationFactory("network.expand_arcs").apply_to(m) 48 49#Feed Specifications to heater 50m.fs.heater.inlet.flow_mol.fix(x["heater_inlet_molflow"]) # mol/s 51m.fs.heater.inlet.mole_frac_comp[0, "benzene"].fix(x["heater_inlet_benzene_molfrac"]) 52m.fs.heater.inlet.mole_frac_comp[0, "toluene"].fix(x["heater_inlet_toluene_molfrac"]) 53m.fs.heater.inlet.pressure.fix(x["heater_inlet_pressure"]) # Pa 54m.fs.heater.inlet.temperature.fix(x["heater_inlet_temperature"]) # K 55 56# Unit model specifications 57m.fs.heater.outlet.temperature.fix(x["heater_outlet_temperature"]) # K 58m.fs.flash.heat_duty.fix(x["flash_heat_duty"]) # W 59m.fs.flash.deltaP.fix(x["flash_pressure_drop"]) # Pa 60 61#Flowsheet Initialization 62def function(unit): 63 unit.initialize(outlvl=1) 64 65opt = SolverFactory('ipopt') 66seq = SequentialDecomposition() 67seq.options.select_tear_method = "heuristic" 68seq.run(m, function) 69 70# Solve the flowsheet using ipopt 71opt = SolverFactory('ipopt') 72solve_status = opt.solve(m) 73 74#Assign the simulation result from IDAES model to FOQUS output values 75f["flash_liq_molflow"] = value(m.fs.flash.liq_outlet.flow_mol[0]) 76f["flash_liq_benzene_molfrac"] = value(m.fs.flash.liq_outlet.mole_frac_comp[0,"benzene"]) 77f["flash_liq_toluene_molfrac"] = value(m.fs.flash.liq_outlet.mole_frac_comp[0,"toluene"]) 78f["flash_liq_temperature"] = value(m.fs.flash.liq_outlet.temperature[0]) 79f["flash_liq_pressure"] = value(m.fs.flash.liq_outlet.pressure[0]) 80f["flash_vap_molflow"] = value(m.fs.flash.vap_outlet.flow_mol[0]) 81f["flash_vap_benzene_molfrac"] = value(m.fs.flash.vap_outlet.mole_frac_comp[0,"benzene"]) 82f["flash_vap_toluene_molfrac"] = value(m.fs.flash.vap_outlet.mole_frac_comp[0,"toluene"]) 83f["flash_vap_temperature"] = value(m.fs.flash.vap_outlet.temperature[0]) 84f["flash_vap_pressure"] = value(m.fs.flash.vap_outlet.pressure[0]) 85f["heater_heat_duty"] = value(m.fs.heater.heat_duty[0])
Note
ipopt will need to be available in your environment. This should be available through the following command during the generic install of IDAES in the environment:
idaes get-extensionsOnce the model is solved, the values of flowsheet output variables are assigned to the node output variables.
Click the Run button to run the python script and check the node output variables section, note that their values should have changed.
It should be noted that the values within Node Input Variables can be changed as per user’s requirement, to run different cases.
Note
For more information on installing IDAES, along with building and solving IDAES models, refer to the IDAES documentation: https://idaes-pse.readthedocs.io/en/stable/index.html
This tutorial demonstrates the capability of simulating IDAES based process models in FOQUS. However, optimization problems can also be solved using IDAES in FOQUS, by providing the required degrees of freedom.
It is recommended that FOQUS and IDAES must be installed in the same conda environment for this example to run successfully.
The complete FOQUS file (FOQUS_IDAES_Example.foqus), that includes the IDAES model,
is located in: examples/tutorial_files/IDAES.
The examples/ directory refers to the location where the FOQUS examples were installed, as described in Install FOQUS Examples.